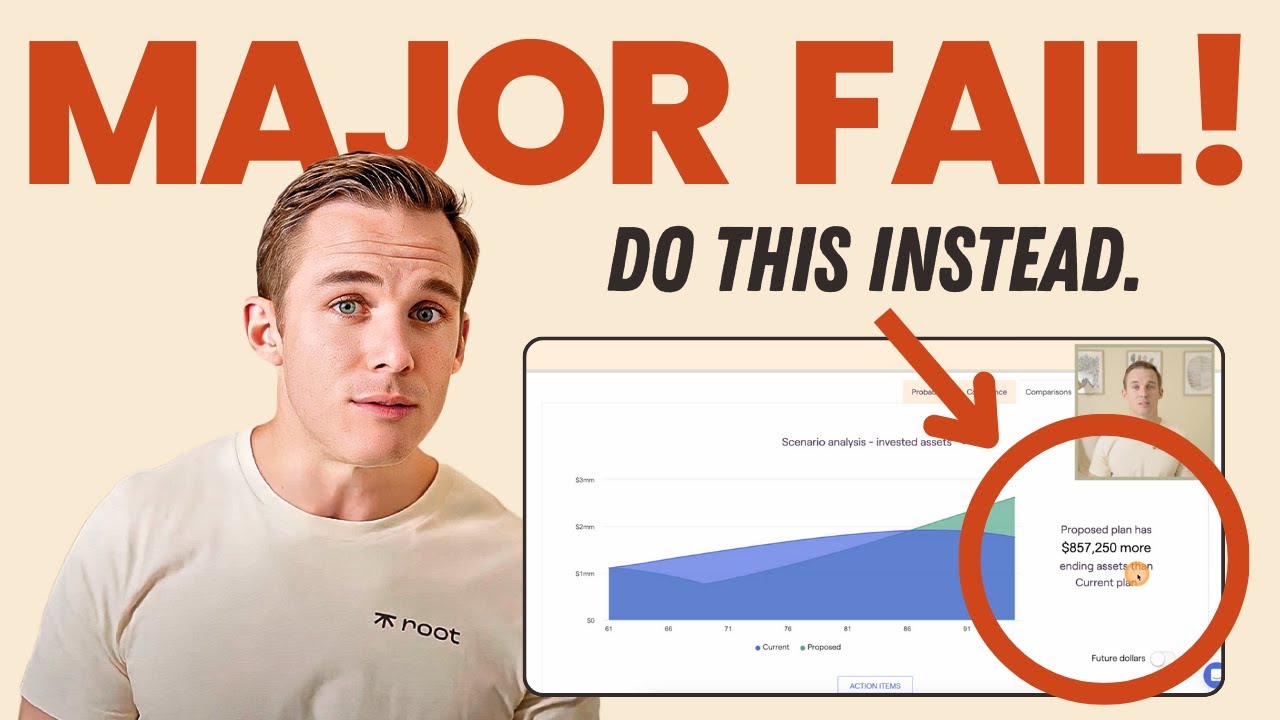
Are you considering delaying your Social Security benefits until age 70 based on the belief that the break-even age is around 80 or 81? This might not be the best decision for you. In this video, James delves into a real client example to illustrate how decisions around Social Security can have profound implications on your financial plan.
Greg and Sherry, a couple aged 62, approached us with the goal of retiring immediately. They had a substantial portfolio, including 401(k)s, Roth IRAs, savings, and a paid-off home. Their aim was to maintain a $6,000 monthly lifestyle throughout retirement, accounting for healthcare expenses and taxes.
Key Assumptions:
Aggressive Investment Mix: 90% in diversified stocks, 10% in various bonds, projecting an 8.8% annual return.
Longevity: Projected lifespan until age 95.
The traditional analysis suggests that delaying Social Security until age 70 yields greater lifetime benefits. However, a detailed examination reveals a critical factor often overlooked – the impact of delayed Social Security on the overall financial plan.
Initial Analysis: If Greg and Sherry chose to collect Social Security at 62, their portfolio would maintain a healthy trajectory, allowing them to meet their expenses over the years. The net effect was positive.
Counterintuitive Results: When they considered delaying Social Security until age 70, the seemingly increased benefits came at a cost. The strain on their portfolio during the years without Social Security income significantly offset the potential gains, resulting in over $400,000 less at the end of their lifetime.
James emphasizes the often-underappreciated role of the rate of return on investments. In a hypothetical scenario with a lower growth rate of 6.3%, delaying Social Security until age 70 proved to be more financially advantageous, adding over $850,000 to their overall wealth.
While the break-even age is commonly cited as a justification for delaying Social Security, the analysis reveals a more nuanced reality. Even with the additional wealth created by delaying, the break-even age could still be around 86.
The decision on when to collect Social Security is complex and interconnected with various aspects of your financial plan. A holistic approach, considering factors like investment growth, tax implications, and other income sources, is crucial. There is no one-size-fits-all solution, and a personalized analysis based on individual circumstances is imperative.
=======================
Learn the tips & strategies to get the most out of life with your money.
Get started today → [ Ссылка ]
Get access to the retirement software I use in this video and more → [ Ссылка ]
🔔 Make sure to subscribe here to be notified for future videos!
[ Ссылка ]
_ _
👥 Make sure to connect with us on all socials below → [ Ссылка ]
⏱Timestamps:⏱
0:00 Delaying social security?
0:30 A case study
3:30 Things to consider
6:00 Calculating portfolio withdrawal percentage
8:09 SS at 62 versus 67
11:55 The analysis
13:50 Opportunity cost
14:28 No one size fits all
16:48 The impact of growth rate
18:16 The break-even age
Other videos we think you'll like:
About Root: [ Ссылка ]
Worried about retirement?
Start here: [ Ссылка ]