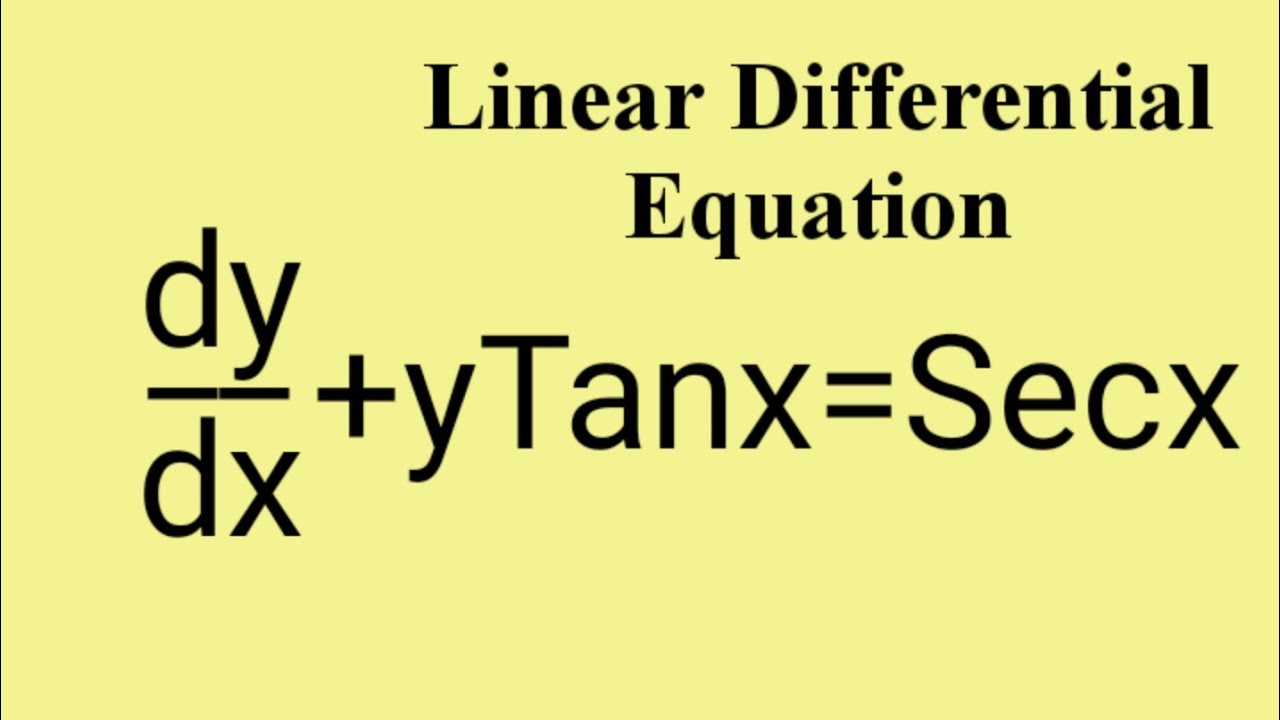#lineardifferentialequationoffirstorder
Hello, Everyone!
Here is a video of a differential equation problem, which is linear. Have a little patience and watch the video till end.
My hearty thanks to all the subscribers, supporters, viewers and well-wishers❤
With Love,
Chinnaiah Kalpana🍁
Note:
* Ordinary Differential Equation(ODE):
A differential equation is said to be ordinary, if the derivatives in the equation have reference to only a single independent variable.
* Linear differential equations of first order(Linear differential equation):
A differential equation of the form
dy/dx + P y = Q ___(1)
where, P and Q are constants or functions of X alone (i.e., not of y) is called a linear differential equation of the first order in the dependent variable y. Here, the dependent variable and its derivatives occur only in the first degree.
Also, if Q(x)=0 for all x,
then (1) is called Non-Homogeneous.
* Working rule for solving Linear differential equation:
1. Rewrite the given equation in standard form (i.e., dy/dx+Py=Q).
2. Identify P and Q (It may be either constants or functions of x alone).
3. Determine the integrating factor.
i.e., I.F. = exp(∫Pdx)
4. Write the general solution as
y(I.F)= ∫Q.(I.F)dx+c.
* exp(log f(x))=f(x),
exp[nlogf(x)]=exp[log (f(x))^2]=[f(x)]^2,
exp[-log f(x)] = exp[log (f(x))^-1] = [f(x)]^-1 = 1/f(x)
For more such videos 👇
[ Ссылка ]
I'm on Instagram👇
[ Ссылка ]
Stay tuned to 'Maths Pulse'.
Get rid of 'Maths Phobia'.
Have a happy learning!
#differentialequations #mathspulse #chinnaiahkalpana #engineeringmathematics #bscmaths #maths #math