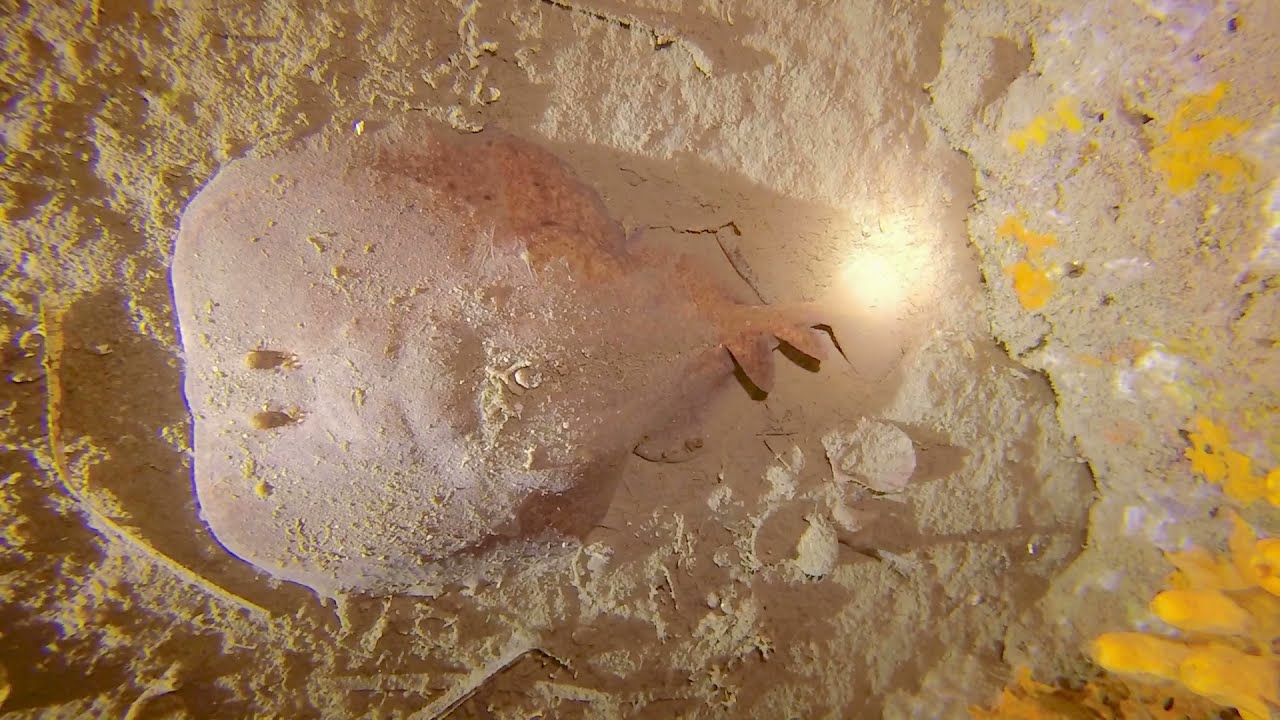
Nocturnal and solitary, the marbled electric ray can often be found lying thesea floor buried except for its eyes and spiracles. This slow-moving predator feeds almost exclusively on small bony fishes, which it ambushes from the bottom and subdues with strong electric bursts. It defends itself by turning towards the threat, swimming in a loop, or curling up with its underside facing outward, while emitting electric shocks to drive off the prospective predator. Its paired electric organs are capable of producing 70–80 volts of electricity. This species is aplacental viviparous, with the developing embryos sustained by yolk and histotroph ("uterine milk") produced by the mother. Mating takes place from November to January, and females bear litters of 3–32 pups every other year after a gestation period of 9–12 months. The newborn ray is immediately capable of using electricity to hunt.
The electric shock delivered by a marbled electric ray can be severe but is not directly life-threatening. Its electrogenic properties have been known since classical antiquity, when live rays were used to treat conditions such as chronic headaches. This and other electric ray species are used as model organisms in biomedical research. Various coastal demersal fisheries take the marbled electric ray as bycatch; captured rays are usually discarded as they have little commercial value. The impact of fishing on its population is uncertain, and thus International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) has listed this ray under Data Deficient. In the Mediterranean Sea, it remains the most common electric ray and in some areas may be increasing in number.
Source: [ Ссылка ]
————
Adriatic Sea, Archipel of Dalmatia in Croatia 2021