C data types tutorial example explained
#C #data #types
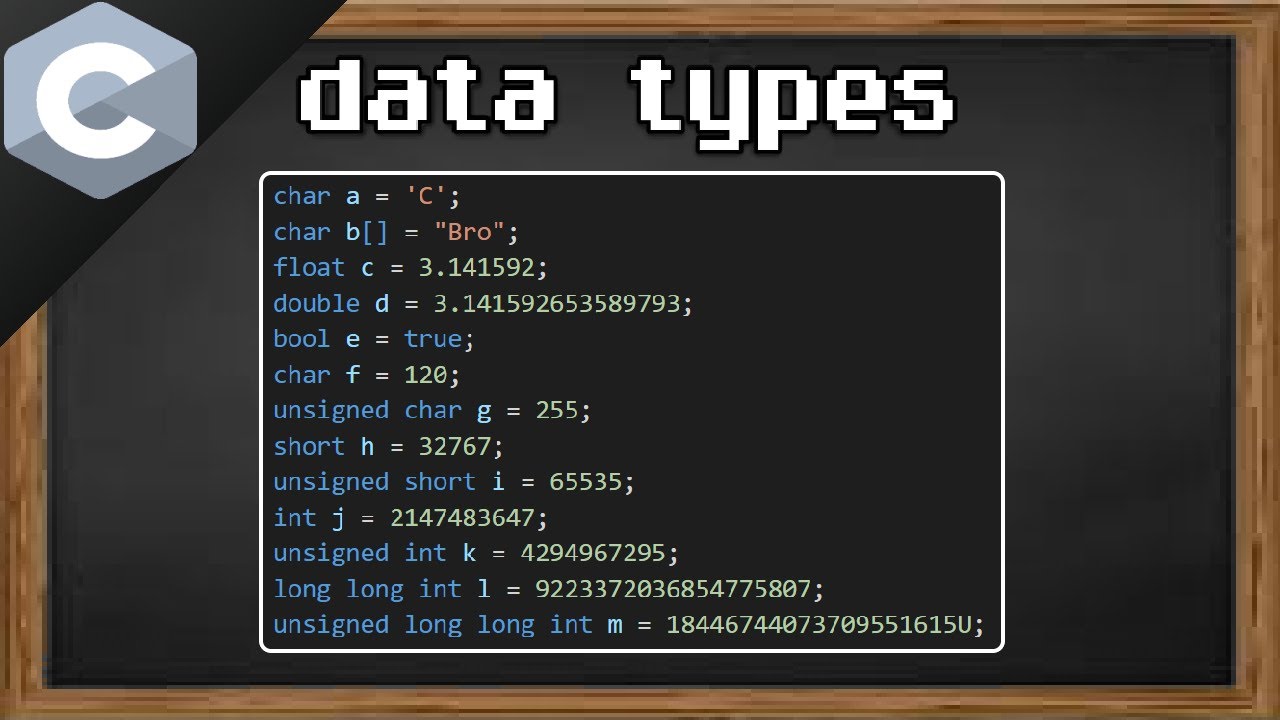
char a = 'C'; // single character %c
char b[] = "Bro"; // array of characters %s
float c = 3.141592; // 4 bytes (32 bits of precision) 6 - 7 digits %f
double d = 3.141592653589793; // 8 bytes (64 bits of precision) 15 - 16 digits %lf
bool e = true; // 1 byte (true or false) %d
char f = 120; // 1 byte (-128 to +127) %d or %c
unsigned char g = 255; // 1 byte (0 to +255) %d or %c
short h = 32767; // 2 bytes (−32,768 to +32,767) %d
unsigned short i = 65535; // 2 bytes (0 to +65,535) %d
int j = 2147483647; // 4 bytes (-2,147,483,648 to +2,147,483,647) %d
unsigned int k = 4294967295; // 4 bytes (0 to +4,294,967,295) %u
long long int l = 9223372036854775807; // 8 bytes (-9 quintillion to +9 quintillion) %lld
unsigned long long int m = 18446744073709551615U; // 8 bytes (0 to +18 quintillion) %llu
printf("%c\n", a); // char
printf("%s\n", b); // character array
printf("%f\n", c); // float
printf("%lf\n", d); // double
printf("%d\n", e); // bool
printf("%d\n", f); // char as numeric value
printf("%d\n", g); // unsigned char as numeric value
printf("%d\n", h); // short
printf("%d\n", i); // unsigned short
printf("%d\n", j); // int
printf("%u\n", k); // unsigned int
printf("%lld\n", l); // long long int
printf("%llu\n", m); // unsigned long long int