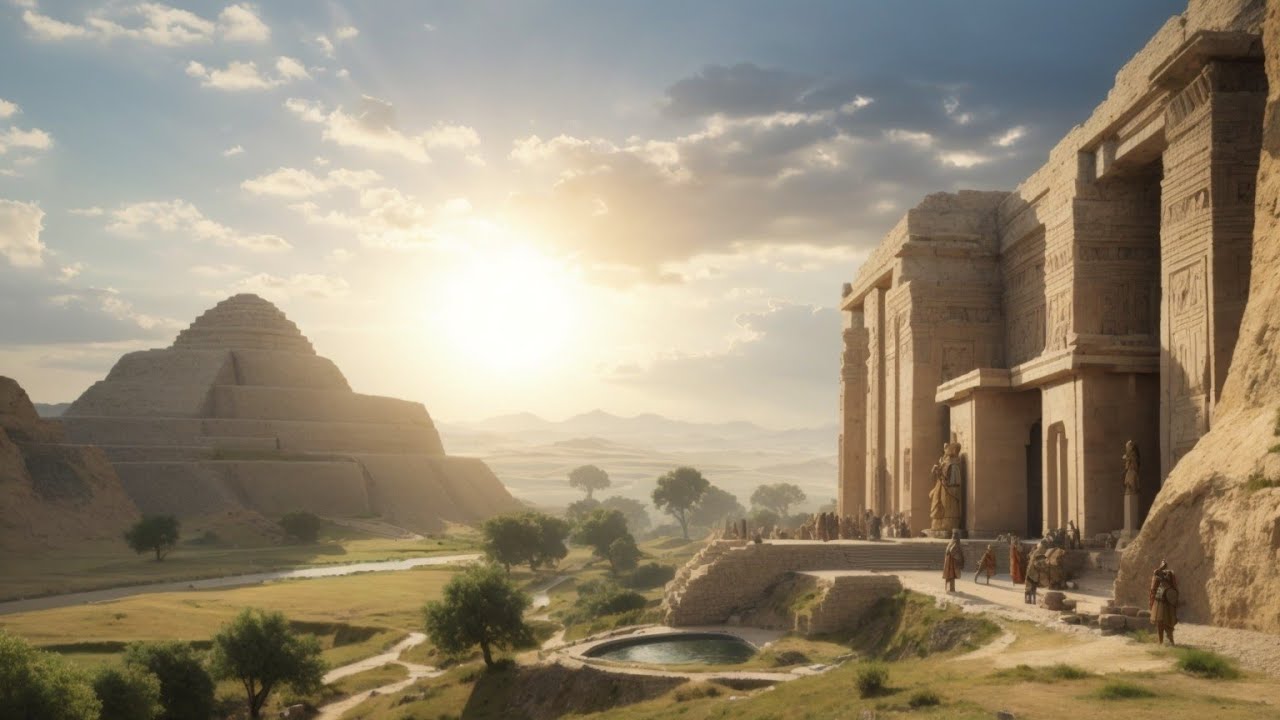
The Zapotec civilization, an ancient and influential Mesoamerican culture, holds a significant place in the rich tapestry of human history. Flourishing in the region that is now Oaxaca, Mexico, the Zapotecs are renowned for their advanced societal and architectural achievements, as well as their lasting impact on art, culture, and governance.
The Zapotec civilization emerged around 1400 BCE and reached its zenith between 500 BCE and 800 CE. Their heartland, the Valley of Oaxaca, was marked by a diverse geography that ranged from fertile valleys to mountainous terrain. This topographical variation influenced their development, allowing the Zapotecs to adapt and thrive in different ecological niches.
One of the most remarkable aspects of the Zapotec civilization was their architectural prowess. The ancient city of Monte Albán, perched on a high plateau, serves as a testament to their engineering brilliance. This urban center was meticulously planned, with impressive temples, pyramids, plazas, and residences, all arranged in a precise grid pattern. The grandeur of Monte Albán reflected the Zapotecs' skill in manipulating their environment to create both functional and awe-inspiring structures.
The Zapotecs were also masterful artisans, creating intricate pottery, jewelry, and textiles that depicted their culture and beliefs. Their artwork often incorporated symbolic motifs, representations of deities, and mythological narratives. The famous Zapotec urns, adorned with detailed carvings and paintings, provide valuable insights into their daily life, rituals, and spiritual practices.
Religion played a crucial role in Zapotec society. Their belief system revolved around a pantheon of gods and goddesses, each representing different natural elements and celestial phenomena. Ceremonial centers and temples were constructed to honor these deities and facilitate religious rituals. The Zapotecs also practiced ancestor veneration, believing that deceased family members maintained a connection with the living and could influence their lives.
The Zapotecs are perhaps most renowned for their system of hieroglyphic writing, known as the Zapotec script. This script, inscribed on stelae, ceramics, and codices, represented a significant step in the development of writing in the Americas. While our understanding of the Zapotec script is limited, researchers continue to decipher its meaning, shedding light on the civilization's history and culture.
Despite their achievements, the Zapotec civilization faced challenges, including conflicts with neighboring groups such as the Mixtecs. The decline of Monte Albán around 800 CE marked the waning of their urban center's influence. However, the Zapotec culture persisted in various forms across the region.
Today, the descendants of the Zapotecs continue to inhabit Oaxaca and surrounding areas, maintaining a connection to their ancestral heritage. The legacy of the Zapotec civilization lives on in their artistic traditions, cultural practices, and the ongoing archaeological discoveries that offer insights into their past.
In conclusion, the Zapotec civilization stands as a testament to human ingenuity and adaptability. Their architectural achievements, intricate artwork, religious beliefs, and contributions to early writing systems have left an indelible mark on Mesoamerican history. The enduring legacy of the Zapotecs serves as a reminder of the remarkable achievements of ancient cultures and their lasting impact on our understanding of the human story.
#ZapotecCivilization #AncientMesoamerica #ZapotecCulture #PreColumbianArt #ArchaeologicalWonders #OaxacaHistory #ZapotecArchitecture #CulturalHeritage #MesoamericanCivilizations #HistoricalExploration #IndigenousLegacy #ZapotecTraditions #AncientCivilizations #ArchaeologyDiscoveries #CulturalAchievements #OaxacanHeritage