Gastric metaplasia is an important preneoplastic (Precancerous) lesion. Sometimes metaplasia is with displasia in the same area ; but standart endoscopes generally can not visualize the metaplastic and displastic area. Displasia has 30 % cancer risk . If the patient has metaplasia and high risk for gastric cancer ( smoking, alcohol, smoked meat , cancer in the family etch. ) we have to use advance diagnostic endoscopic system with magnification can chromoendoscopy.
Diagnosis of Metaplasia (Cell Exchange ) in the Stomach
with Advanced Endoscopy
Dear viewers, I'd like to talk about metaplasia today.
Gastric metaplasia; metaplasia of the stomach. Metaplasia means cell exchange. So the normal gastric cell inside the stomach goes away, instead the cells come from the intestine and settle inside the stomach. This is important because the gastric cell is resistant to acid and external factors, but when the intestinal cells from the intestine settle in the stomach, they are affected by stomach acid and begin to deteriorate over tim e. Again, external factors contribute to this, and therefore these metaplastic cells, i.e. the intestinal cells that are located inside the stomach, begin to deteriorate over time. That's what we call dysplasia. Cell disruption. Dysplasia is different from metaplasia. There is now a significant problem with dysplasia, there is a trend towards cancer, and about 1 to 3 percent of all metaplastic patients show progression towards cancer. Therefore, we would like to detect this at an early stage.
There are also two types of dysplasia; low-grade dysplasia, high-grade dysplasia. After high-grade dysplasia comes early stage cancer. If we detect metaplasia at an early stage, or detect it in the dysplasia phase, we have a chance to save the patient by removing it. So if metaplasia is more on the road as it progresses towards cancer, or if it's an early-stage gastric cancer if it's not spreading, then we go in endoscopically and remove it (this tissue). Of course, here's the important thing; advanced endoscopes capture metaplasia very easily, standard endoscopes do not easily see metaplasia or dysplasia. However, advanced endoscopes with the help of magnification properties, also endoscopes with such special lighting methods called chromoendoscopy have the ability to see these metaplastic, dysplastic lesions very easily. And people who have a relative who has gastric cancer in their past, who eats very salty food with a risk of cancer in their family, who also eat smoked food, should definitely have advanced endoscopy and such people's family probably has metaplasia and has to be fallowed in the future.
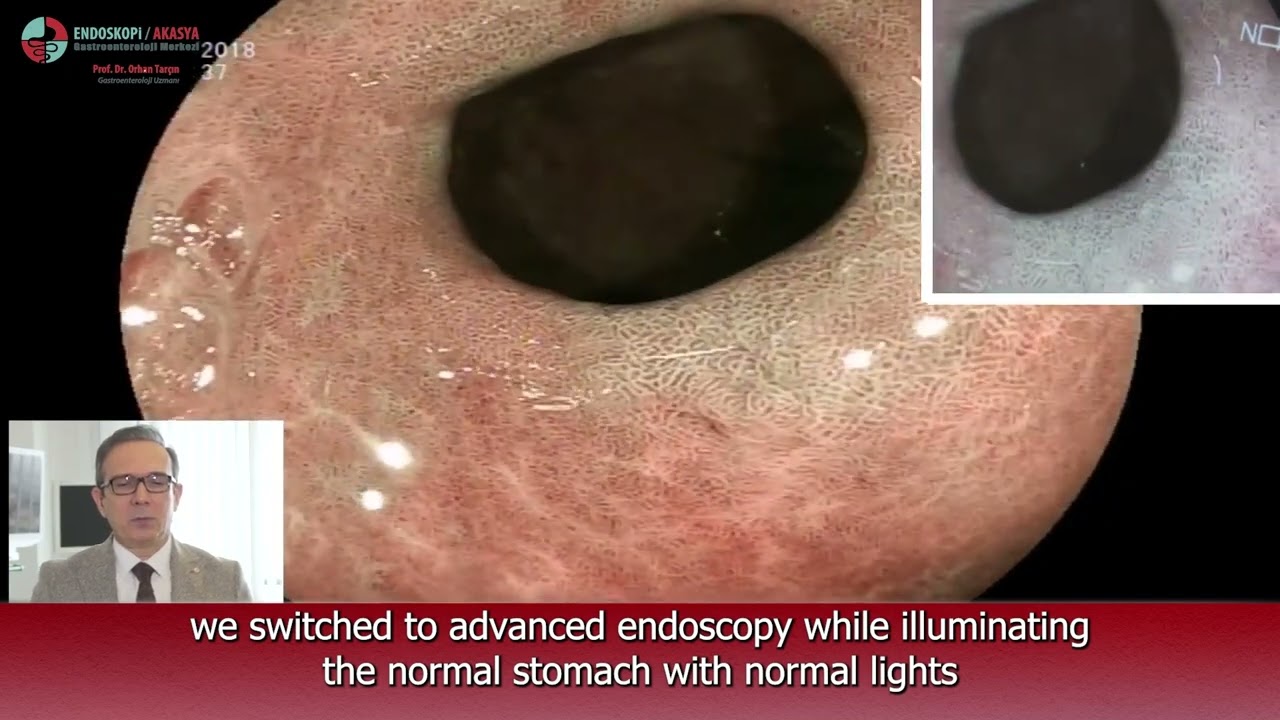
Now, I'd like to give an example of one of these groups of metaplastic patients. Now, we'd like to investigate whether our patient you saw here had metaplasia in a random gastric biopsy that was previously taken. So what are the dimensions of metaplasia, sometimes when there is metaplasia, there is dysplasia with it, and there is also early stage cancer. As you can see here, we switched to advanced endoscopy while illuminating the normal stomach with normal lights and are looking for metaplasia with BLI mode (Blue Laser Imaging) mode.
Now we move on to another mode called LCI mode. It gives off pink light, and here at 2:00 o clock, you see metaplastic tissues, you see areas. It looks more dented here than the inner membrane of the normal stomach. Of course, we need to see the limits of these, we need to see the bottoms of these metaplastic fields. We're examining the bases one by one with advanced endoscopy. Standard endoscopy cannot see the base of metaplasia, but advanced endoscopes see its base, see vascular changes, see its architectural texture.
Yes, as you can see here, it's a metaplastic field again. Yes, we're looking at the base, we're looking at its vascular structure; It's quite normal, so if it was dysplastic, the micro-architecture would be broken. And then there would be tortiosis in these vascular structures, there would be curvature, they would expand, and at the same time the structure would deteriorate. And in the next stage, they would be thinned out and disappeared. That's what we detect with advanced endoscopes, and if there's a deterioration, we raise it, go under it, scrape it out without surgery. But in the old days, if there was dysplasia, we used to operate this group of patients on every occasion. But now, thanks to diagnosing dysplasia, metaplasia, and early stage cancer, we can scrape (resect) them off before the patient goes to the gastric operation and the cancer progresses or turns into cancer.
Here you see the inner surface of the stomach. We scan the inner surface of the stomach millimetrically. We switched to the small intestine, and there are finger like protrusions in the small intestine. #metaplasia #dysplasia #advancedendoscopy