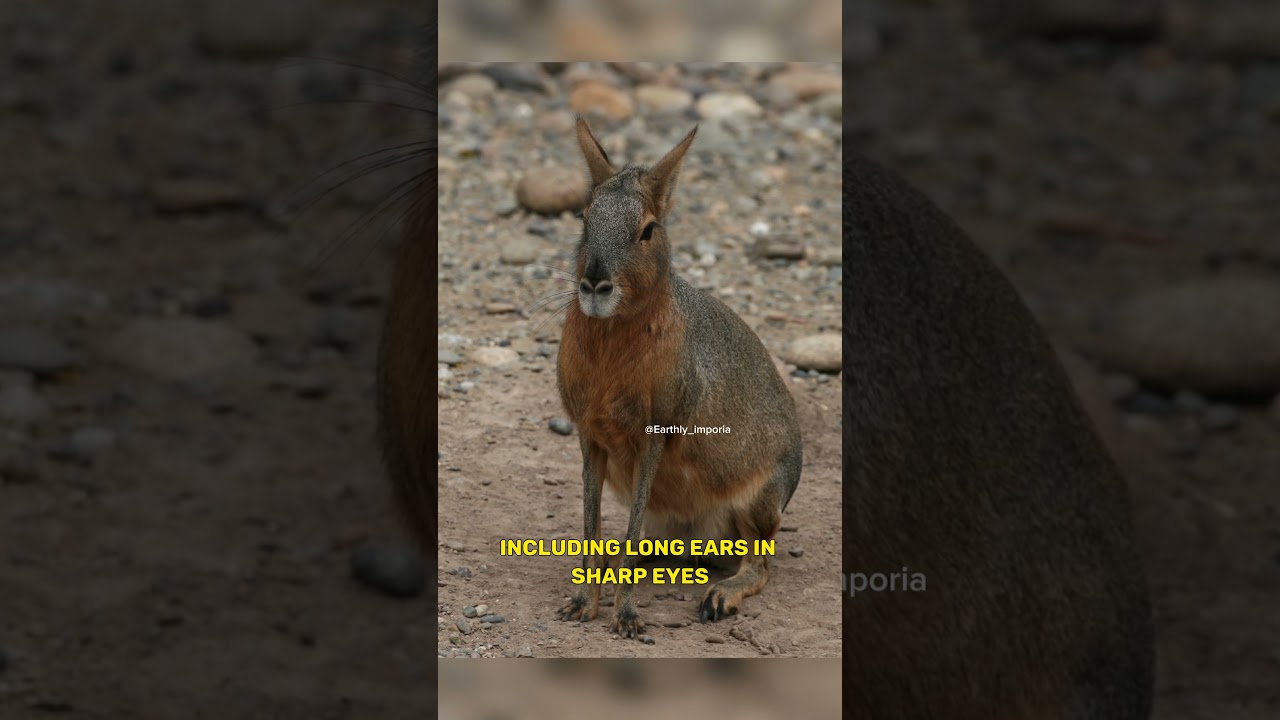
The Patagonian mara, also known as the Patagonian cavy or hare, is a large herbivorous rodent native to Argentina. These unique animals have a striking appearance, resembling a mix between a rabbit and a deer, with long legs, long ears, and sharp eyes. They are highly social creatures, often living in monogamous pairs or small family groups, and communicate through vocalizations and scent markings.
Patagonian maras are well-adapted to their grassland and scrubland habitats, where they graze on grasses, herbs, and foliage. They are also known to eat fruits and seeds occasionally. These rodents are fast runners, capable of reaching speeds of up to 29 miles per hour (46 km/h) to escape predators.
In terms of reproduction, female Patagonian maras give birth to one to three precocial young, known as pups, after a gestation period of about 90 days. The pups are relatively developed at birth and can move around shortly after.
While not currently endangered, Patagonian maras face threats from habitat loss and hunting in some areas. Conservation efforts are in place to protect their populations. These animals play an important ecological role in their ecosystem by grazing on vegetation, which helps maintain grasslands and promotes plant diversity.


























































![[Jigokuraku на русском] Kamihitoe [Onsa Media]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/c57qBspO2kc/mqdefault.jpg)










![[4K] SIARGAO to CAGAYAN DE ORO! Ultimate Travel Guide & Journey Experience!](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/SBr1T1ci9jQ/mqdefault.jpg)

