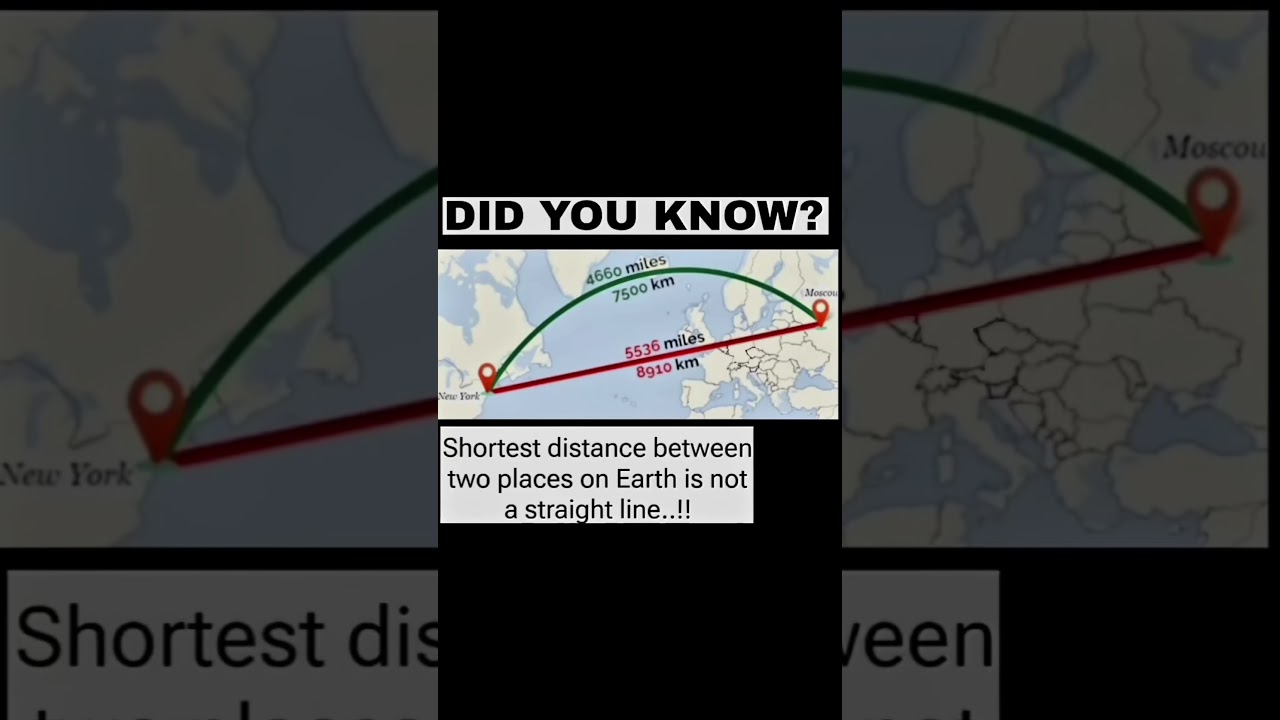
That's correct! The shortest distance between two points on the Earth's surface is not a straight line, but a great circle route, also known as an orthodrome. This is because the Earth is approximately spherical in shape, so the shortest path between two points on its surface will follow the curvature of the Earth.
Imagine you're flying from New York to London. If you were to fly in a straight line, you'd end up in the ocean! Instead, planes follow a great circle route, which takes them north over Canada and then across the Atlantic, following the curvature of the Earth. This route is longer in terms of straight-line distance, but shorter in terms of actual distance traveled, because it follows the Earth's surface.
This concept is important in navigation, aviation, and even space exploration, where calculating the shortest distance between two points on a sphere (or near-spherical shape) is crucial for efficient routing and travel.