Data catalog and metadata management are crucial aspects of data engineering and data governance. They play a significant role in ensuring that data is discoverable, understandable, and effectively utilized across an organization. Here's an overview of these concepts:
Data Catalog:
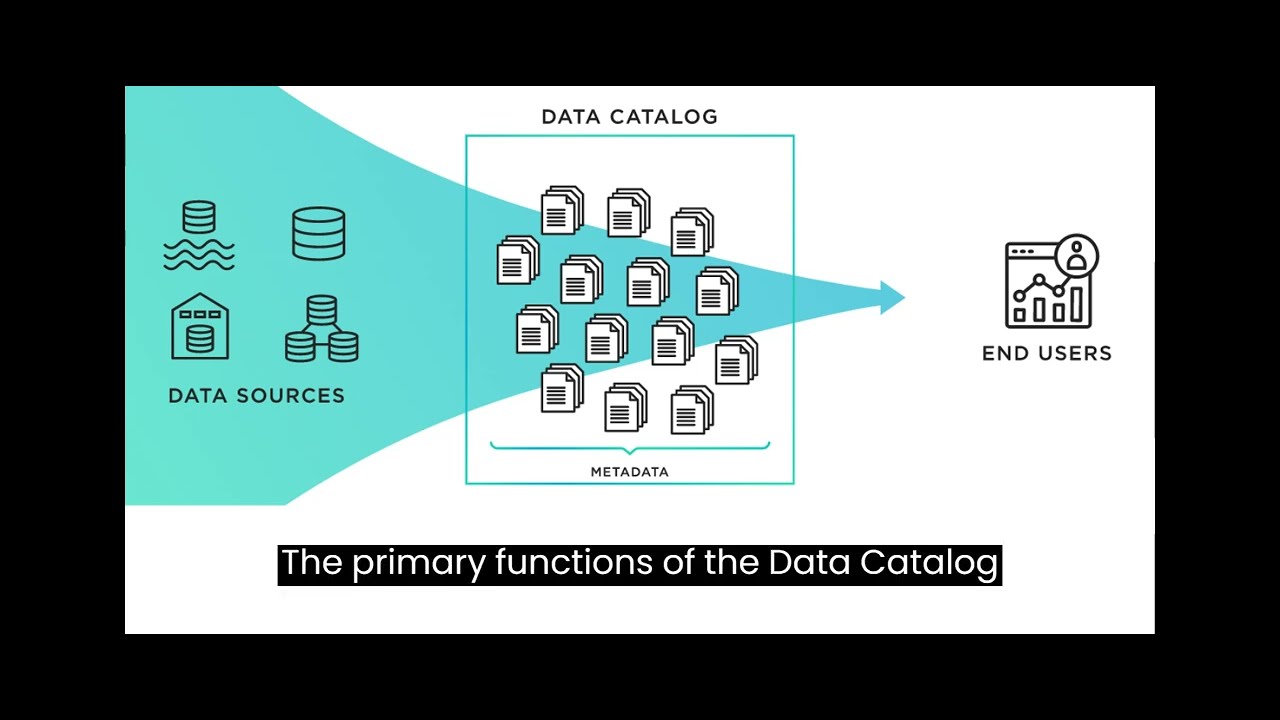
A data catalog is a centralized repository that stores metadata about the data assets within an organization. This metadata includes information about the data's structure, location, lineage, ownership, and usage. The primary functions of a data catalog are:
Data Discovery: It allows users to search for and discover data assets within an organization. This is essential for data analysts, data scientists, and business users to find the data they need.
Data Lineage: It provides information about the origin and transformation of data, helping users understand how data flows through the organization and how different datasets are related.
Data Usage and Access: Users can see who has access to the data and how it is being used. This is crucial for data governance and compliance.
Metadata Management: It stores metadata related to data assets, including descriptions, data quality, and data classification. This helps users understand the data's meaning and quality.
Collaboration: Data catalog tools often support collaboration features, enabling data users to comment, rate, and share insights about data assets.
Data Governance: Data catalogs play a vital role in data governance by enforcing data access policies, data stewardship, and ensuring compliance with regulations.
Metadata Management:
Metadata is data about data. In the context of data engineering, metadata management involves collecting, storing, and managing metadata related to all aspects of data, including its source, structure, transformations, usage, and lineage. The goals of metadata management are:
Data Understanding: Metadata helps users understand what the data means, where it comes from, and how it's structured.
Data Lineage: It tracks the history of data, showing how it has been transformed from source to destination.
Data Quality: Metadata can include information about data quality metrics and indicators, helping organizations assess and improve data quality.
Data Governance: Metadata management is crucial for enforcing data governance policies, data classification, and ensuring compliance with regulations.
Data Integration: Metadata aids in the integration of data from various sources by providing a common understanding of data elements.
Data Security: Metadata can include access controls and security information, helping to protect sensitive data.
In a data engineering context, metadata is often generated and captured as part of the ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) process. Metadata is stored in a metadata repository, which can be part of a data catalog or a separate system.
Effective data catalog and metadata management are essential for organizations to leverage their data assets efficiently, ensure data quality, maintain data governance, and enable data-driven decision-making. These tools and practices are especially important as data volumes and complexity continue to grow.