Created by [ Ссылка ] and shown with permission.
This is an illustration for the Quantum Physics Encyclopedia at [ Ссылка ].
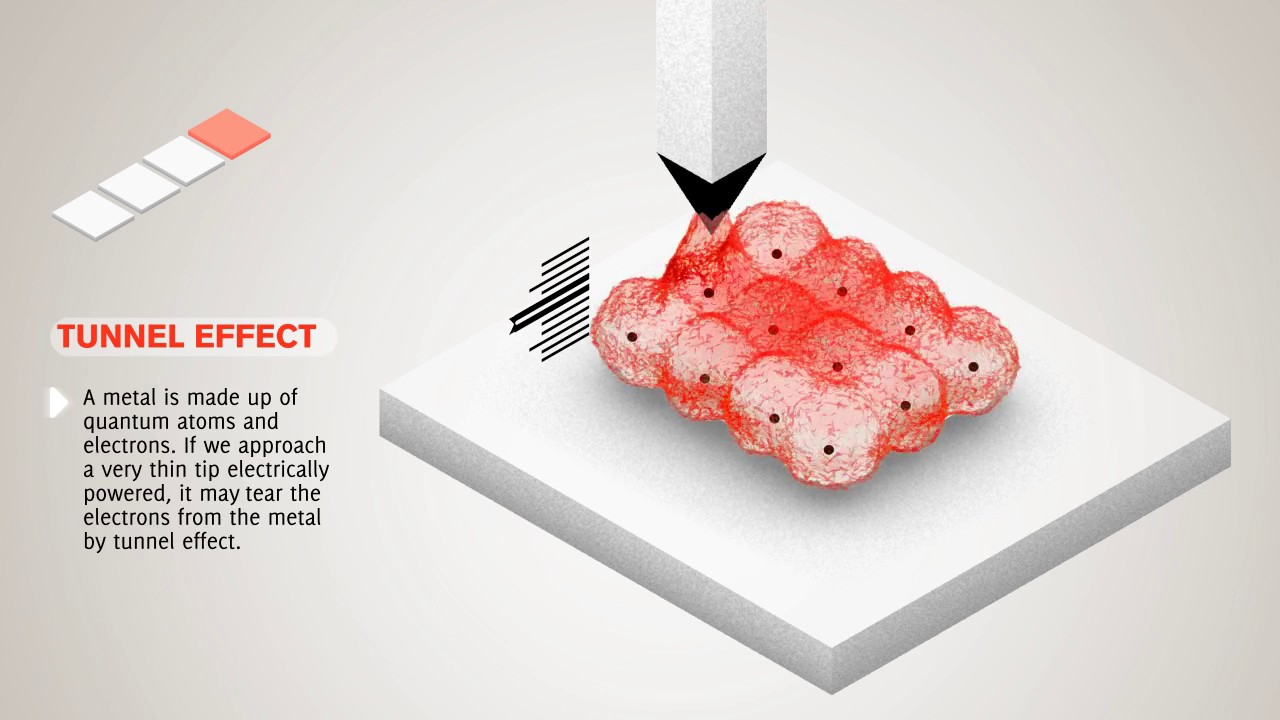
This animated video shows the quantum tunneling effect and then, how tunneling is put to use in a scanning tunneling microscope. Quantum tunneling is the ability of a quantum particle to breach a barrier, even one which, according to the laws of classical physics, it should have insufficient energy to breach. It disappears on one side of the barrier and instantaneously appears on the other. Calculations also show that the particle disappears on one side and appears on the other without traversing the distance in between.
Scanning tunneling microscopes allow us to form images of objects as small as atoms, a task not possible with microscopes that rely on light. The scanning tunneling microscope (STM) has a stylus with a tip made of a single atom to probe or “feel” materials atom by atom. The microscope creates an image based on what the probe has felt.
In the STM, electrons tunnel across a gap (the barrier) between the tip of the probe and the surface being examined. Depending on the type of STM, the electrons might be generated by either the tip or the surface being examined. As they tunnel, the electrons generate an electrical signal. This signal is strengthened by an amplifier and fed into an electronic display screen that forms an image of the surface being examined.