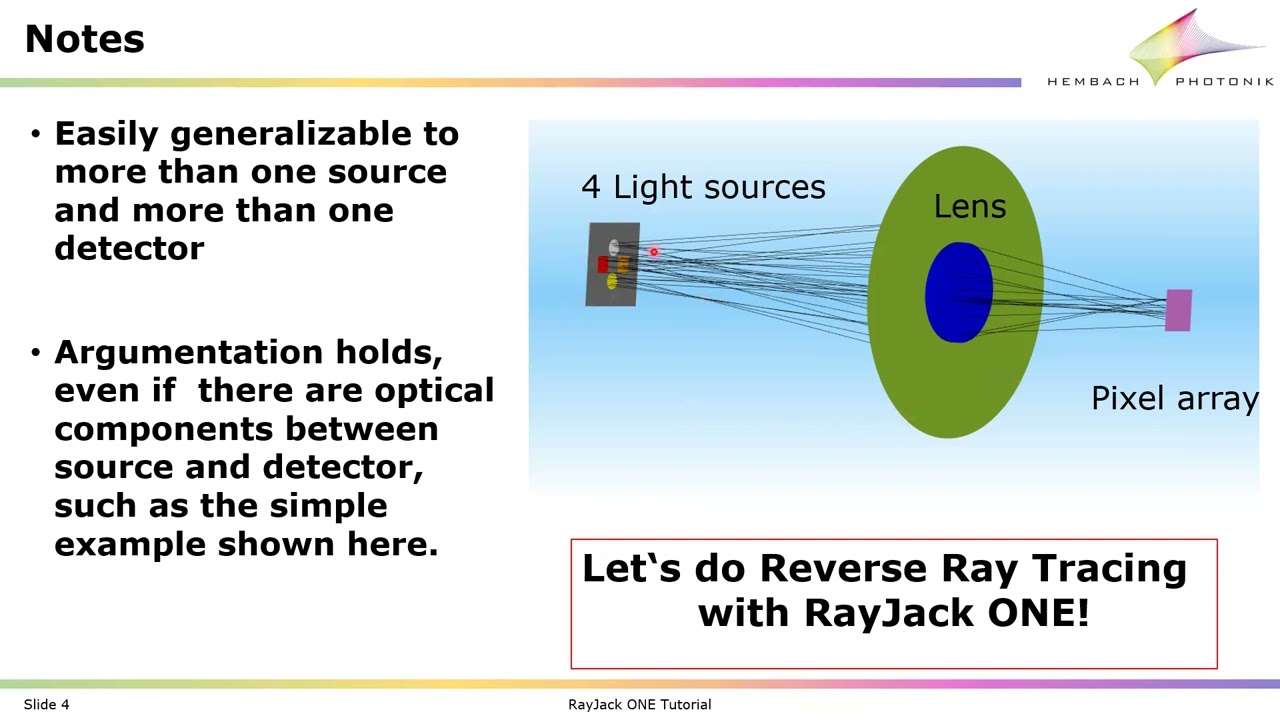
When simulating optical systems (including illumination systems), one normally creates the rays on light sources. The rays are then traced through the optical system and analyzed on detectors. In some cases it is more efficient to interchange the roles of sources and detectors: rays are started from the detector and are evaluated on the sources. This method is called reverse or backward ray tracing. The video explains the underlying radiometric concepts. As an example, both a forward and a reverse ray trace are performed in RayJack ONE for a simple optical system, leading to the same results.
Reverse tracing is very often used in infrared simulations, where objects are thermal radiators. RayJack ONE offers library functions to compute radiant exitances of thermal sources, making infrared simulations very convenient.