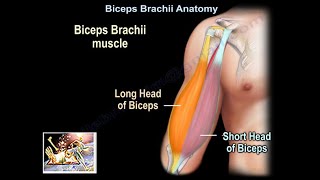
Dr. Ebraheim’s educational animated video describes anatomy of the biceps brachii muscle.
Follow me on twitter:
[ Ссылка ]
Find me on Instagram @OrthoInitiative
Biceps Brachii Anatomy
The biceps brachii is a two-headed muscle that lies on the upper arm between the shoulder and the elbow. The long head of the biceps tendon arises from the supraglenoid tubercle. The biceps tendon is intraarticular structure. The tendon also arises from the superior aspect of the glenoid labrum slightly posterior. The long head of the biceps then passes underneath the transverse humeral ligament in the bicipital groove between the lesser and greater tuberosity of the humerus. The area where the biceps tendon passes through the bicipital groove is a common site of bicipital tendonitis and anterior shoulder pain. The long head of the biceps tendon lies between the two tendons of the supraspinatus and subscapularis muscles. Occasionally the biceps tendon dislocates from the groove such as with a subscapularis tendon rupture. Rupture of the long head of the biceps tendon may occur at the bicipital groove and the muscle then moves towards the elbow (Popeye muscle). The short head of the biceps arises from the coracoid process of the scapula. The long and short heads then join together and inset into the proximal radius at the elbow region in an area called the radial tuberosity. The biceps tendon insertion foot print is ribbon shaped on the ulnar aspect of the radial tuberosity. Some consider the bicipital aponeurosis to be another insertion for the distal biceps tendon. The bicipital aponeurosis is attached to the deep fascia on the medial side of the forearm proximally. The brachial artery and median nerve is deep to the bicipital aponeurosis with the medial cubital vein the medial cubital vein passing above it. This area is important in surgery and in written exams. The biceps muscle may become ruptured at its insertion site into the radial tuberosity. The tendon will retract up into the upper arm causing a bump or “Popeye” deformity. The biceps muscle is innervated by the musculocutaneous nerve which runs under the biceps. The lateral antebrachial cutaneous nerve originates from the musculocutaneous nerve and lies between the brachialis and the biceps muscles. The musculocutaneous nerve also supplies these two muscles. The coracobrachialis muscle also originates from the coracoid process medial to the short head of the biceps. Injury to the lateral antebrachial cutaneous nerve may occur when treating a distal biceps tendon rupture with surgery. When treating a humeral shaft fracture with an IM rod, the use of anterior screws distally in the humerus may cause injury to the musculocutaneous nerve. Injury to the nerve results in loss of sensation along the radial aspect of the forearm. The function of the biceps muscle is to supinate the forearm and flex the elbow. Herniated disc at C4-C5 level will affect the C5 nerve root which will affect the function of the biceps muscle. Biceps reflex is primarily C5.