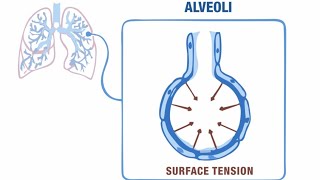
Lung surfactant is a mixture of lipids and proteins produced by type II alveolar cells in the lungs. Its primary function is to reduce surface tension within the alveoli, preventing their collapse during exhalation and maintaining lung compliance. This allows for efficient gas exchange by keeping the alveoli open and preventing them from sticking together. Surfactant deficiency can lead to respiratory distress syndrome, especially in premature infants..
Example of surfactants
1)DPPC: Dipalmitolyphosphatidylcholine
2)PG: phosphatidylglycerol@med micro




](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/hqJIx0tAEX0/mqdefault.jpg)
![[BNHA] ALL FOR ONE clips for edits](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/40ZZ7lwJzNA/mqdefault.jpg)



















































![Top 5 Luxury Travel Destinations [4K]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/HsLTylcfSE4/mqdefault.jpg)
![[Bad] - VK наносит ответный удар (Вбросы, ВК Гранты и Comedy Club)](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/1gR5tlf5XPc/mqdefault.jpg)