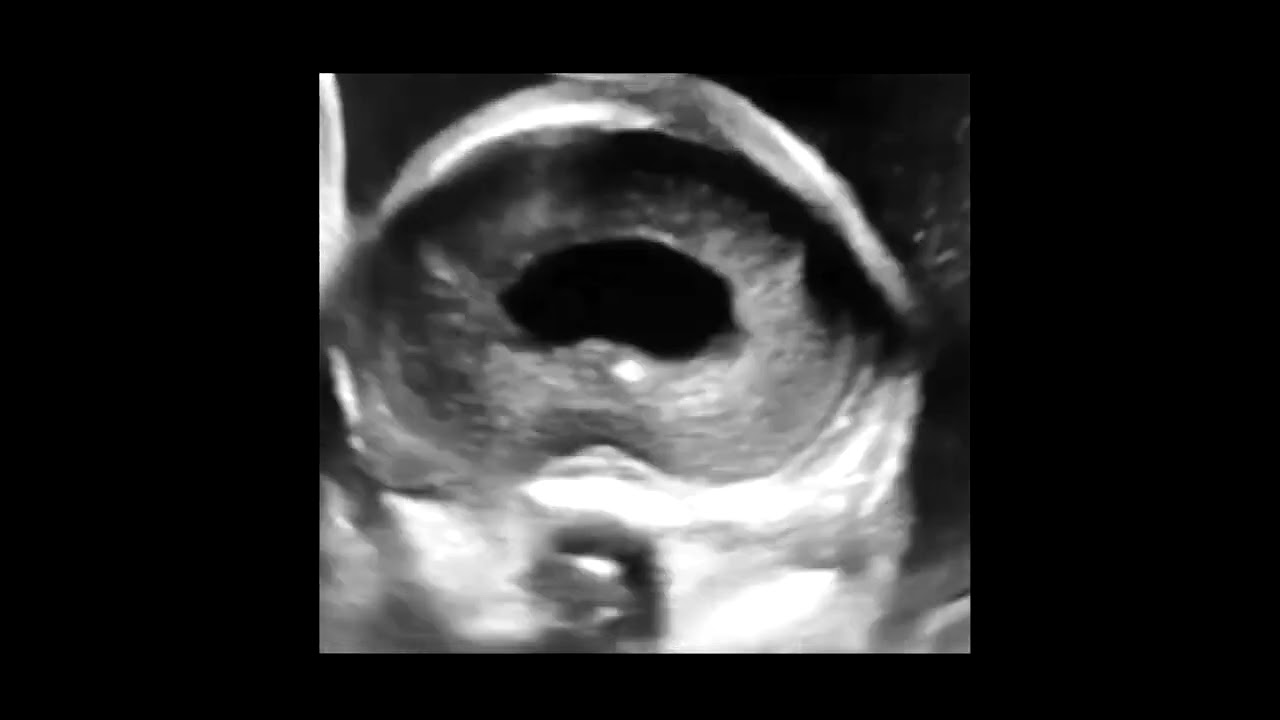
Holoprosencephaly and schizencephaly are both rare brain disorders that can affect brain development.
Holoprosencephaly is a condition in which the forebrain, which is normally divided into two separate hemispheres, fails to divide properly during embryonic development. This results in a range of brain and facial abnormalities, including intellectual disability, seizures, and distinctive facial features such as closely spaced eyes, a small head, and a cleft lip or palate. The severity of holoprosencephaly varies widely, with some individuals experiencing mild intellectual impairment and minimal facial abnormalities, while others may have severe intellectual and physical disabilities.
Schizencephaly, on the other hand, is a disorder in which abnormal clefts or gaps form in the brain's cerebral hemispheres. These clefts can range in size from small to large and may occur in one or both hemispheres. Schizencephaly is often associated with other brain abnormalities such as polymicrogyria, in which the surface of the brain has too many folds and creases, and hydrocephalus, which is an accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain.
Both holoprosencephaly and schizencephaly are thought to be caused by genetic mutations or environmental factors that disrupt brain development in the early stages of embryonic development. Treatment options for both disorders are generally supportive and aimed at managing symptoms such as seizures and developmental delays. In some cases, surgery may be required to address hydrocephalus or other associated brain abnormalities.