(Mantoux test, TB skin test, tuberculosis skin test, tuberculin, PPD test, TST, Mantoux tuberculin skin test)
The standard method of determining whether a person is infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis, performed by injecting 0.1 ml of tuberculin purified protein derivative into the inner surface of the forearm. The injection should be made with a tuberculin syringe, with the needle bevel facing upward. It is an intradermal injection.
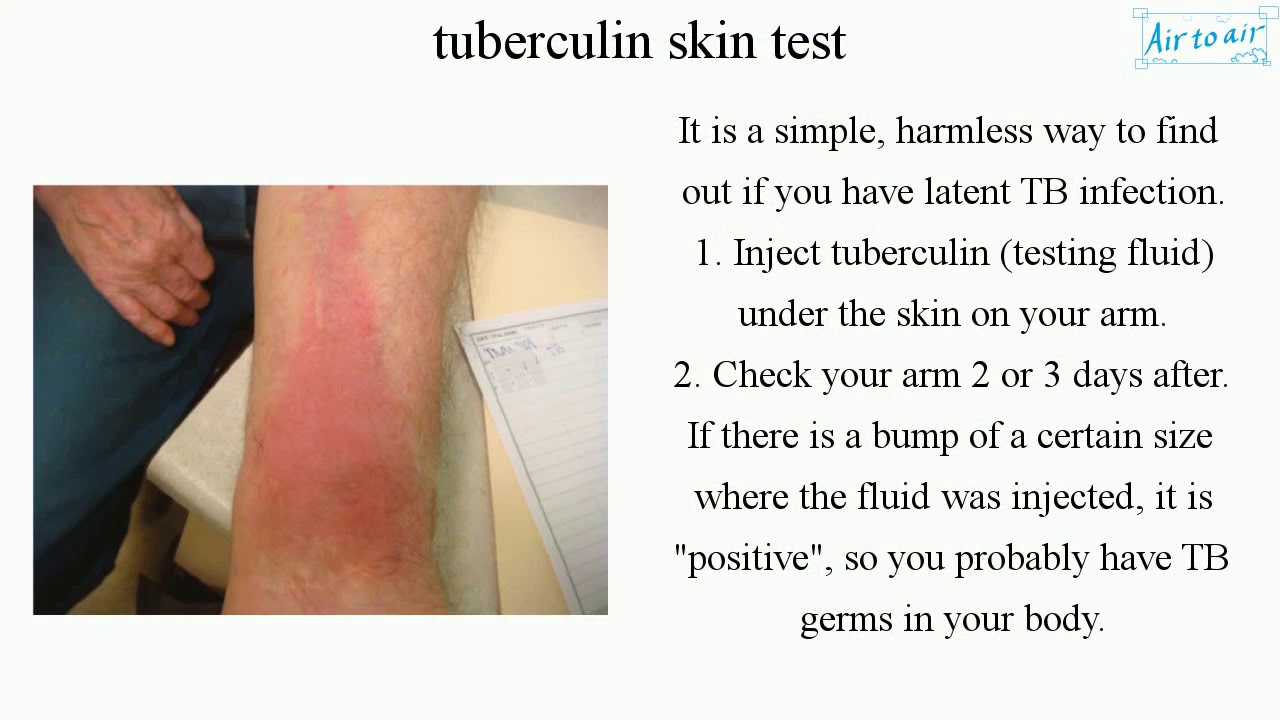
It is a simple, harmless way to find out if you have latent TB infection.
1. Inject tuberculin (testing fluid) under the skin on your arm.
2. Check your arm 2 or 3 days after. If there is a bump of a certain size where the fluid was injected, it is "positive", so you probably have TB germs in your body.
3. You may need further inspection of your body if the result is "positive", followed by appropriate medications.
Even if you have had BCG vaccine, you still can get latent TB infection and active TB disease.
BCG vaccine may help protect young children from getting very sick with TB. This protection goes away as people get older.
BCG vaccine can cause TB skin test "positive", but probably it is from TB germs in your body and not from your BCG vaccine.