Treatments for Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia (AIHA) include:
Initial Treatment:
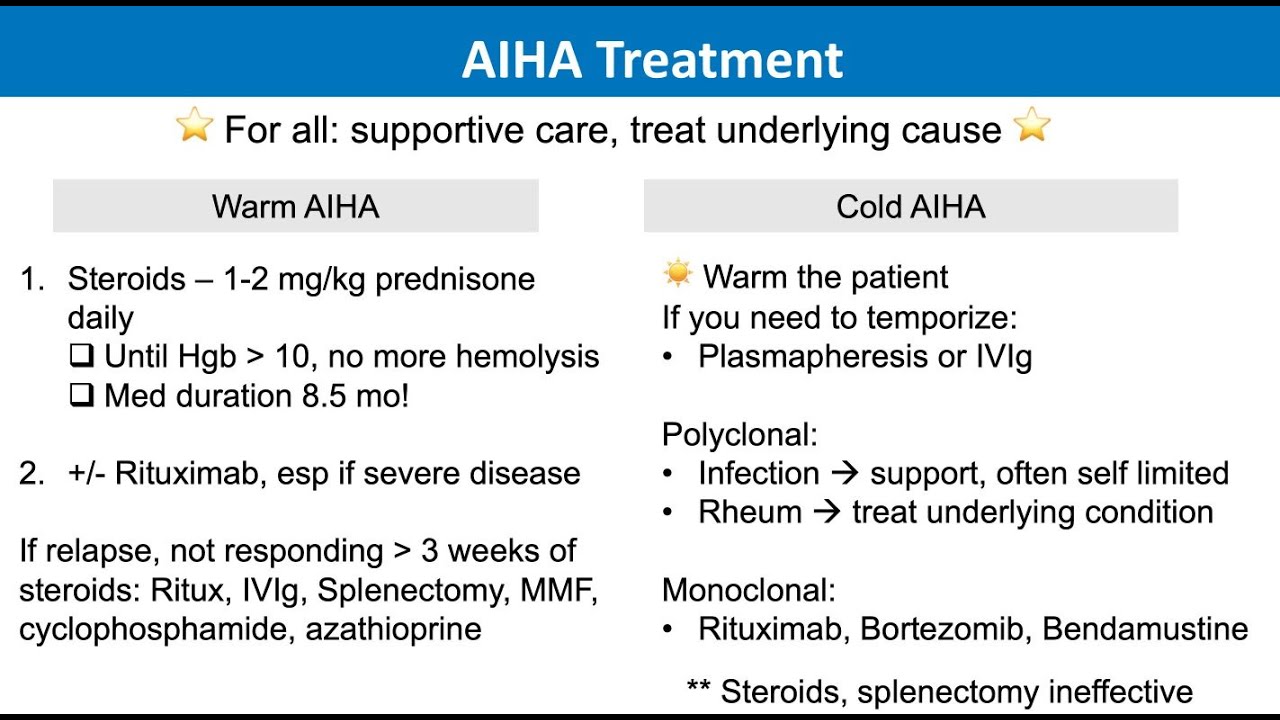
1. Corticosteroids (e.g., prednisone) to reduce antibody production and hemolysis.
2. Immunosuppressive agents (e.g., azathioprine, cyclophosphamide) to suppress the immune system.
Second-Line Treatments:
1. Rituximab (monoclonal antibody) to suppress B cells producing autoantibodies.
2. Splenectomy (surgical removal of the spleen) to reduce antibody production and hemolysis.
3. Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) to neutralize autoantibodies.
Third-Line Treatments:
1. Plasma exchange to remove autoantibodies from the blood.
2. Cyclosporine or tacrolimus to suppress the immune system.
3. Alemtuzumab (monoclonal antibody) to suppress B cells and T cells.
Supportive Care:
1. Blood transfusions to manage anemia.
2. Folic acid supplementation to manage folate deficiency.
3. Iron supplementation to manage iron deficiency.
Emerging Treatments:
1. Complement inhibitors to prevent hemolysis.
2. B-cell depleting therapies to target B cells producing autoantibodies.
3. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in severe cases.
Treatment goals focus on reducing hemolysis, managing anemia, and preventing complications. A healthcare provider will develop a personalized treatment plan based on disease severity and individual needs.
#Hemolyticanemia











![[4K Model Fancam] 걸크러쉬 보미/Girl Crush Bomi/스튜디오 촬영회/세로직캠](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/N5ejLBsEdt8/mqdefault.jpg)




























































