Hypertension pathophysiology, signs and symptoms, complications, and management. Handwritten hypertension full lecture for students taking the USMLE Steps.
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF HYPERTENSION
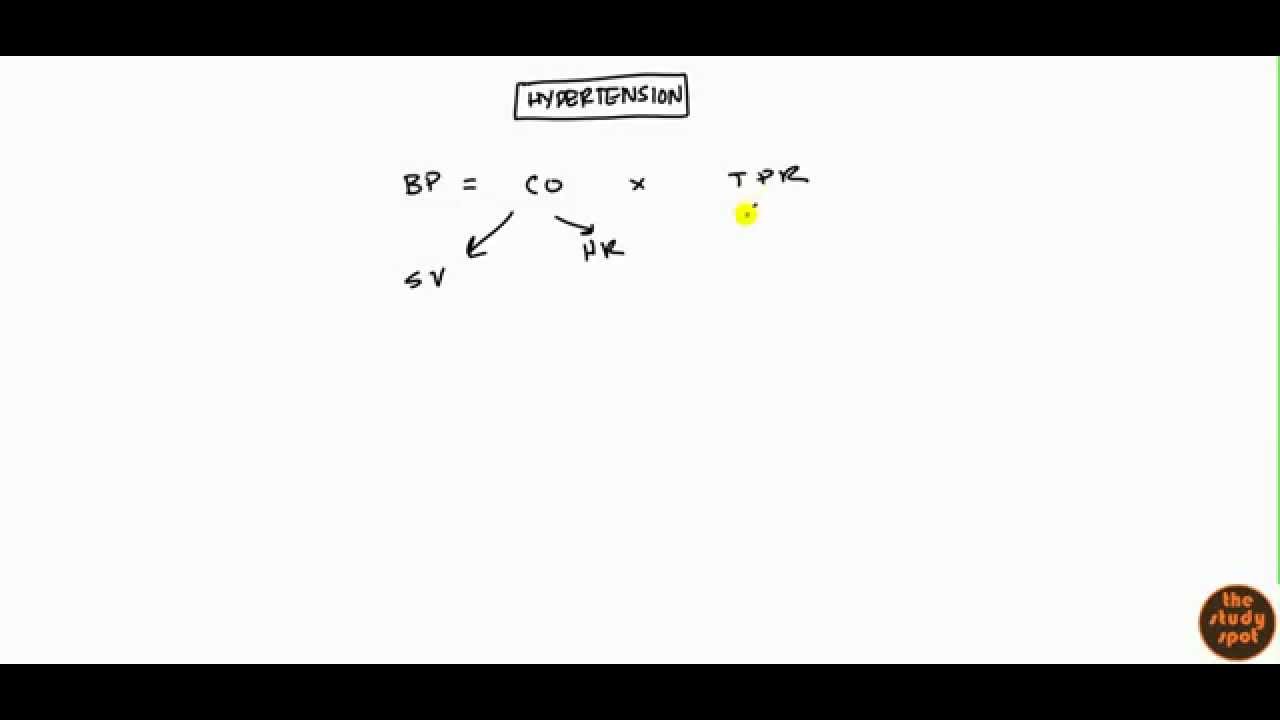
Blood pressure is equal to the cardiac output times the total peripheral resistance. Cardiac output is equal to Stroke Volume times the Heart rate (per minute). Total Peripheral Resistance is determined by the radius of the vessel and compliance.
The primary body systems which help control blood pressure and hypertension is the:
Autonomic Nervous System
alpha1 - vasoconstriction
Beta1 - Increases heart rate
Alpha2 - Decrease sympathetic activity
Renin Aldosterone Angiotensin System
Hormones
Cortisol, Epinephrine, Thyroid and many more.
COMPLICATIONS OF HYPERTENSION
Cardiovascular System complications of hypertension - Left Ventricular Hypertrophy, Confestive Heart Failure, Sudden Cardiac Death
Stroke complcations of hypertension- Infarction, Subarachnoid hemorrhage, Intracerebral hemorrhage, Lacunar infarcts
Renal - Common cause of secondary hypertension, End Stage Renal Disease, Renal Injury, more common in blacks.
Arteries - Atherosclerosis, Claudication
DEFINITION OF HYPERTENSION
Normal Blood pressure is less than 120/80
Pre Hypertension is less than 120-139/80-89
Stage 1 Hypertension is less than 140-159/90-99
Stage 2 Hypertension is greater than 160/100
Isolated Systoilc Hypertension and Isolate Diastolic Hypertension can also occur.
Require minimum of two blood pressure reading over 3 months. Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring is better because can determine night time dip by 10-15%. Also helps distinguish whitecoat hypertension and masked hypertension.
Essential hypertension is when there is no cause identified and is the most common cause. Secondary hypertension can be due to drugs such as OCP, NSAID, TCA, SSRI, Glucocorticoid, EPO, Cyclosporin, Decongestant, Renal causes such as tumor cysts, renal artery stenosis. Adrenal causes of hypertension include high aldosterone, cushings and pheochromocytoma. Endocrine causes of hypertension include hyperthyroidism and hypercalcemia. Aortic coarcation, pre-eclampsia, eclampsia are also other causes of hypertension.
EVALUATION
No specific symptoms can help you diagnose hypertension.
Check BMI, Blood pressure in both arms, Fundoscope, Bruits, Thryoid, murmurs (loud S2 and S4 gallop). Also perform a full Cardiovascular and Neurological examination.
LABS
Renal labs such as urinalysis and albuminuria. ALso rule out metabolic syndrome by checking blood glucose, cholesterol, LDL, HDL, and TAGs. Electrolytes such as Na, K, Calcium.
TREATMENT
Initial treatment for pre hypertension is lifestyle intervention. For hypertension it can help decrease dosage of drug required. Weight reduction alone can decrease blood pressure by 5-20mmHg/10kg. Ideal BMI is less than 25.
Decrease salt intake can also help control hypertension by decrease salt to less than 6g per day.
Dietary Approach to Stop Hypertension (DASH) Diet is high in fruits and vegetables and low in fat can help lower hypertension by 8 to 14mmHg.
Physical activity can also help decrease hypertension by 4-9mmHg.
Pharmacological therapy is used when blood pressure is greater than 140/90. If african american than start with Thiazide and Calcium Channel Blockers, while ACE Inhibitors and ARB are better for patients with Renal disease, Diabetes, Chronic Kidney disease.
Beta Blockers for patients with ischemic heart disease and heart failure. Alpha blocker for patients with





























































![مراقب باش از کجا میخری! معرفی برترین و معتبرترین صرافی های ارز دیجیتال جهان از نظر امنیت [2023]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/WDPh4EO3Fjo/mqdefault.jpg)











