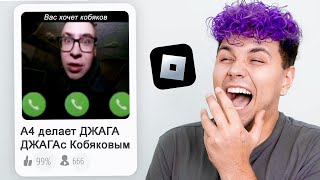
The Persian daric was a gold coin which, along with a similar silver coin, the siglos, represented the bimetallic monetary standard of the Achaemenid Persian Empire.
Cyrus the Great (550–530 BC) introduced coins to the Persian Empire after 546 BC, following his conquest of Lydia and the defeat of its king Croesus, who had put in place the first coinage in history. It seems Cyrus initially adopted the Lydian coinage as such, and continued to strike Lydia's lion-and-bull coinage.
Darius I (521–486 BC) introduced a new thick gold coin which had a standard weight of 8.4 grams, equaling in value 20 silver coins. The gold used in the coins was of very high quality with a purity of 95.83% and it bore the image of the Persian king or a great warrior armed with a bow and arrow.
The Achaemenid Empire issued coins from 520 BCE–450 BCE to 330 BCE. The Persian daric was the first gold coin which, along with a similar silver coin, the siglos represented the first bimetallic monetary standard. It seems that before the Persians issued their own coinage, a continuation of Lydian coinage under Persian rule is likely. Achaemenid coinage includes the official imperial issues (Darics and Sigloi), as well as coins issued by the Achaemenid provincial governors (satraps), such as those stationed in Asia Minor.