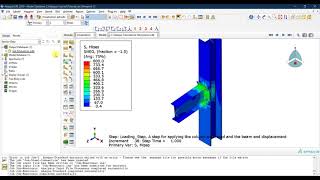
Main Distribution Board Wiring (MDB) 3-phase wiring diagram.
Dear Sir, Thanks for watching my videos. If you have any questions write in the comment box. Don’t forget to like and share. For more updates please subscribe to our channel Learning EEE Animations, and get a notification to press the bell icon.
#EEE Animations
#Md. Sahinur Rahman (Sozol)
Incoming Power Supply:
Three-Phase Power Lines (L1, L2, L3): These are the three live wires carrying alternating current from the power source (e.g., transformer or generator).
Neutral Wire (N): Completes the electrical circuit and carries current back to the power source.
Earth/Ground Wire (E): Provides a path for fault currents to prevent electrical shocks and protect equipment.
Busbars:
Three-Phase Busbars: Copper or aluminum bars that distribute power to various circuits. There are typically three busbars for the three phases (L1, L2, L3).
Neutral and Earth Busbars: Separate busbars for neutral and earth connections, ensuring that all circuits are properly grounded.
Circuit Breakers:
Main Circuit Breaker: Protects the entire system by shutting off power in case of a fault.
Sub-Circuit Breakers: Control and protect individual circuits or groups of circuits. These can be miniature circuit breakers (MCBs) or molded case circuit breakers (MCCBs).
Meters and Monitoring Devices:
Voltage, Current, and Power Meters: Measure the voltage, current, and power consumption on each phase.
Energy Meters: Track the total energy consumed by the system.
Surge Protection Devices (SPDs):
Surge Arresters: Protect the MDB and connected equipment from voltage spikes and surges.
Wiring Diagram Description:
Incoming Power Connection:
The three-phase power lines (L1, L2, L3) enter the MDB and are connected to the main circuit breaker.
The neutral wire (N) and earth wire (E) are connected to their respective busbars.
Busbar Distribution:
From the main circuit breaker, the three-phase lines are connected to the three busbars (one for each phase).
The neutral and earth busbars are connected to the incoming neutral and earth wires.
Outgoing Circuits:
Outgoing circuits are connected to the busbars through sub-circuit breakers. Each outgoing circuit will have connections to one of the phases (L1, L2, or L3), neutral (N), and earth (E).
Single-phase circuits are connected to one phase, neutral, and earth.
Three-phase circuits are connected to all three phases, neutral, and earth.
Metering and Monitoring:
Voltage and current transformers are connected to the phases to monitor the electrical parameters.
The energy meter is connected to track total energy consumption.
Safety Features:
Surge protection devices are connected between the phases and earth to protect against voltage spikes.
Isolation switches are provided for maintenance and emergency shutdowns.
#Electrical Engineering Portal
#Learn Engineering
#Practical Engineering
#Automation Direct
#therapy Engineering Mindset
Business Inquiry Mail: sozol221098@gmail.com




















































![Explore the Futuristic Sci-Fi Cities of a distant future | Sci-Fi Futuristic Music [AI Generated 21]](https://s2.save4k.org/pic/n8DbBXzeeyw/mqdefault.jpg)




![Futuristic Cities - SCI-FI Designed cities [AI Generated Images] [AI Image Generator]](https://s2.save4k.org/pic/hf-XSeSxdrk/mqdefault.jpg)