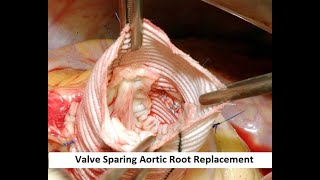
Valve-sparing aortic root replacement (VSARR) is a surgical procedure used to treat aortic valve disease, specifically, a condition called aortic regurgitation (AR) or aortic stenosis (AS). In this procedure, the damaged portion of the aorta (the "root" of the aorta) is replaced while the patient's own aortic valve is left in place and repaired. This is in contrast to a traditional aortic valve replacement, where the entire valve is removed and replaced with a mechanical or biological valve.
The procedure is typically performed using a heart-lung machine, which temporarily takes over the function of the heart and lungs during the surgery. The surgeon will make an incision in the chest, and then carefully remove the damaged portion of the aorta, while preserving the patient's own aortic valve. The new replacement section of the aorta is then sewn into place, and the blood flow is restored to the body.
The main advantage of VSARR over traditional aortic valve replacement is that it allows the patient to keep their own, native valve, which can function more normally and have a longer lifespan. It also reduces the risk of complications and reoperation compared to traditional aortic valve replacement.
It is important to note that not all patients are good candidates for valve-sparing aortic root replacement and that the procedure will be tailored to the specific needs of each patient.













![ПОСТРОИТЬ ТРИ ВИДА ПРОЕКЦИИ ДЕТАЛИ. [construction of three view from a part]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/OMrgMW9Oc1M/mqdefault.jpg)
![TypeScript с 0 до Профи. Полный курс + Практика [2023]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/PYWaUwjofJo/mqdefault.jpg)













































![[PT] Webinar de resiliência costeira | WIOMSA](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/-U11yPiYvuo/mqdefault.jpg)