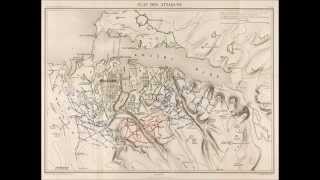
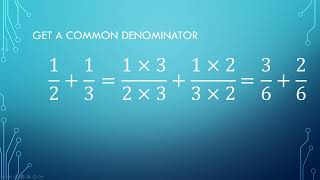The Siege of Sevastopol lasted from September 1854 until September 1855, during the Crimean War. The allies (French, Ottoman, and British) landed at Eupatoria on 14 September 1854, intending to make a triumphal march to Sevastopol, the capital of the Crimea, with 50,000 men. The 56-kilometre (35 mi) traverse took a year of fighting against the Russians. Major battles along the way were Alma (September 1854), Balaklava (October 1854), Inkerman (November 1854), Tchernaya (August 1855), Redan (September 1855), and, finally, Sevastopol (September 1855). During the siege, the allied navy undertook six bombardments of the capital, on 17 October 1854; and on 9 April, 6 June, 17 June, 17 August, and 5 September 1855.
Sevastopol is one of the classic sieges of all time. The city of Sevastopol was the home of the Tsar's Black Sea Fleet, which threatened the Mediterranean. The Russian field army withdrew before the allies could encircle it. The siege was the culminating struggle for the strategic Russian port in 1854–1855 and was the final episode in the Crimean War.
During the Victorian Era, these battles were repeatedly memorialized. The Siege of Sevastopol was the subject of Crimean soldier Leo Tolstoy's Sebastopol Sketches and the subject of the first Russian feature film, Defence of Sevastopol. The Battle of Balaklava was made famous by Alfred, Lord Tennyson's poem "The Charge of the Light Brigade" and Robert Gibb's painting The Thin Red Line, as well as by a panorama of the siege painted by Franz Roubaud. Treating the wounded from these battles were celebrated English nurses Mary Seacole and Florence Nightingale.
The allies (French, Ottoman, and British) landed at Eupatoria on 14 September 1854. The Battle of the Alma (20 September 1854), which is usually considered the first battle of the Crimean War (1853–1856), took place just south of the River Alma in the Crimea. An Anglo-French force under Jacques Leroy de Saint Arnaud and FitzRoy Somerset, 1st Baron Raglan defeated General Alexander Sergeyevich Menshikov's Russian army, which lost around 6,000 troops.
Moving from their base at Balaklava at the start of October, French and British engineers began to direct the building of siege lines along the Chersonese uplands to the south of Sevastopol. The troops prepared redoubts, gun batteries, and trenches.
With the Russian army and its commander Prince Menshikov gone, the defence of Sevastopol was led by Vice Admirals Vladimir Alexeyevich Kornilov and Pavel Nakhimov, assisted by Menshikov's chief engineer, Lieutenant Colonel Eduard Totleben. The military forces available to defend the city were 4,500 militia, 2,700 gunners, 4,400 marines, 18,500 naval seamen, and 5,000 workmen, totalling just over 35,000 men.
The Russians began by scuttling their ships to protect the harbour, then used their naval cannon as additional artillery and the ships' crews as marines. Those ships deliberately sunk by the end of 1855 included Grand Duke Constantine, City of Paris (both with 120 guns), Brave, Empress Maria, Chesme, Yagondeid (84 guns), Kavarna (60 guns), Konlephy (54 guns), steam frigate Vladimir, steamboats Thunderer, Bessarabia, Danube, Odessa, Elbrose, and Krein.
By mid-October 1854, the Allies had some 120 guns ready to fire on Sevastopol; the Russians had about three times as many.
On 17 October 1854 (old style date, 29 October new style)[a] the artillery battle began. The Russian artillery first destroyed a French magazine, silencing their guns. British fire then set off the magazine in the Malakoff redoubt, killing Admiral Kornilov, silencing most of the Russian guns there, and leaving a gap in the city's defences. However, the British and French withheld their planned infantry attack, and a possible opportunity for an early end to the siege was missed.


![[1/2] ЗУБЫ. Структура, формирующая личность](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/pNZ1O58Iuds/mqdefault.jpg)