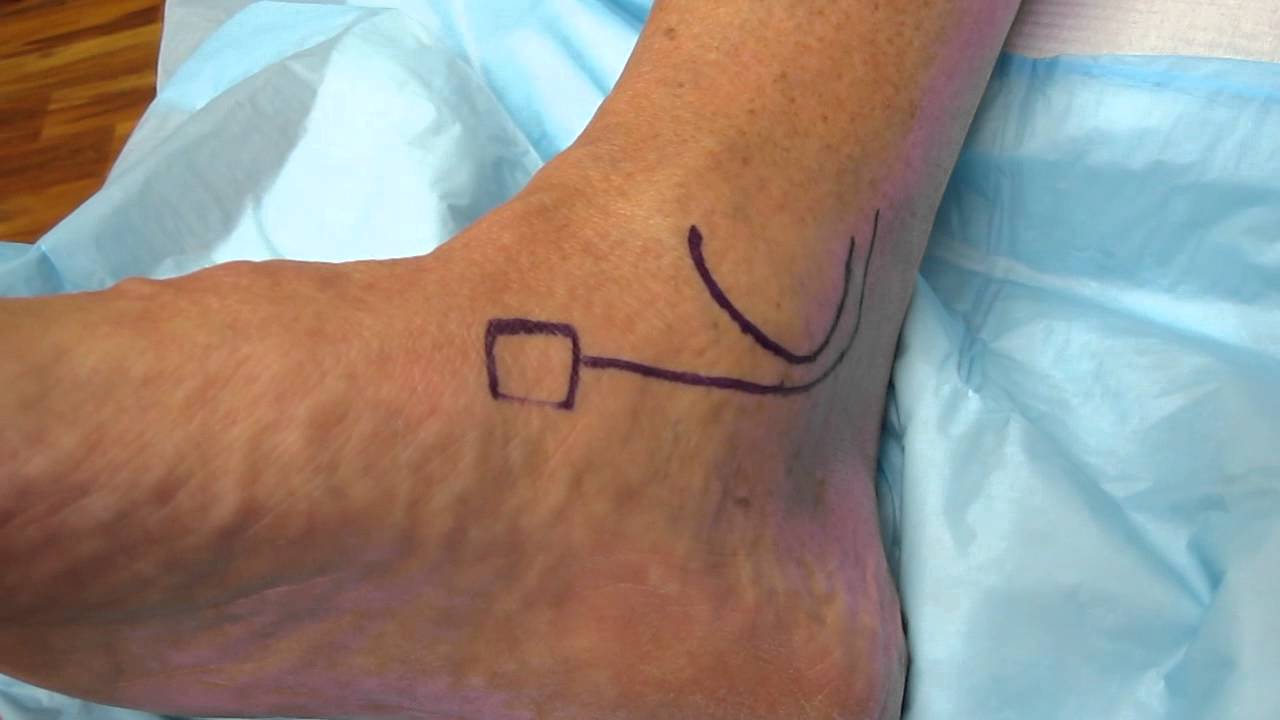
Dr. Stewart reviews the common physical examination findings in a patient with posterior tibial tendon dysfunction. The posterior tibial tendon originates as a muscle in the deep compartment of the leg and courses around the ankle and inserts in the foot. The tendon is the main inverter of the foot and helps to support the arch of the foot. When the tendon is not functioning properly, patients experience pain along the inside of the foot and ankle with swelling and difficulty walking. Pain is also commonly felt on the top and outside of the foot as the subtalar and ankle joints become inflamed from excessive flattening of the foot.


































































![Wiózł cały motor w częściach, okazało się, że jest kradziony! [Celnicy na straży Europy]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/82ta2RoL4pk/mqdefault.jpg)





