Glass Fibers | Manufacturing Process of Glass Fiber | ENGINEERING STUDY MATERIALS
Glass fiber (or glass fibre) is a material consisting of numerous extremely fine fibers of glass.
Glassmakers throughout history have experimented with glass fibers, but mass manufacture of glass fiber was only made possible with the invention of finer machine tooling. In 1893, Edward Drummond Libbey exhibited a dress at the World's Columbian Exposition incorporating glass fibers with the diameter and texture of silk fibers. Glass fibers can also occur naturally, as Pele's hair.
Glass wool, which is one product called "fiberglass" today, was invented in 1932–1933 by Russell Games Slayter of Owens-Corning, as a material to be used as thermal building insulation. It is marketed under the trade name Fiberglas, which has become a genericized trademark. Glass fiber when used as a thermal insulating material, is specially manufactured with a bonding agent to trap many small air cells, resulting in the characteristically air-filled low-density "glass wool" family of products.
Glass fiber has roughly comparable mechanical properties to other fibers such as polymers and carbon fiber. Although not as rigid as carbon fiber, it is much cheaper and significantly less brittle when used in composites. Glass fibers are therefore used as a reinforcing agent for many polymer products; to form a very strong and relatively lightweight fiber-reinforced polymer (FRP) composite material called glass-reinforced plastic (GRP), also popularly known as "fiberglass". This material contains little or no air or gas, is more dense, and is a much poorer thermal insulator than is glass wool.
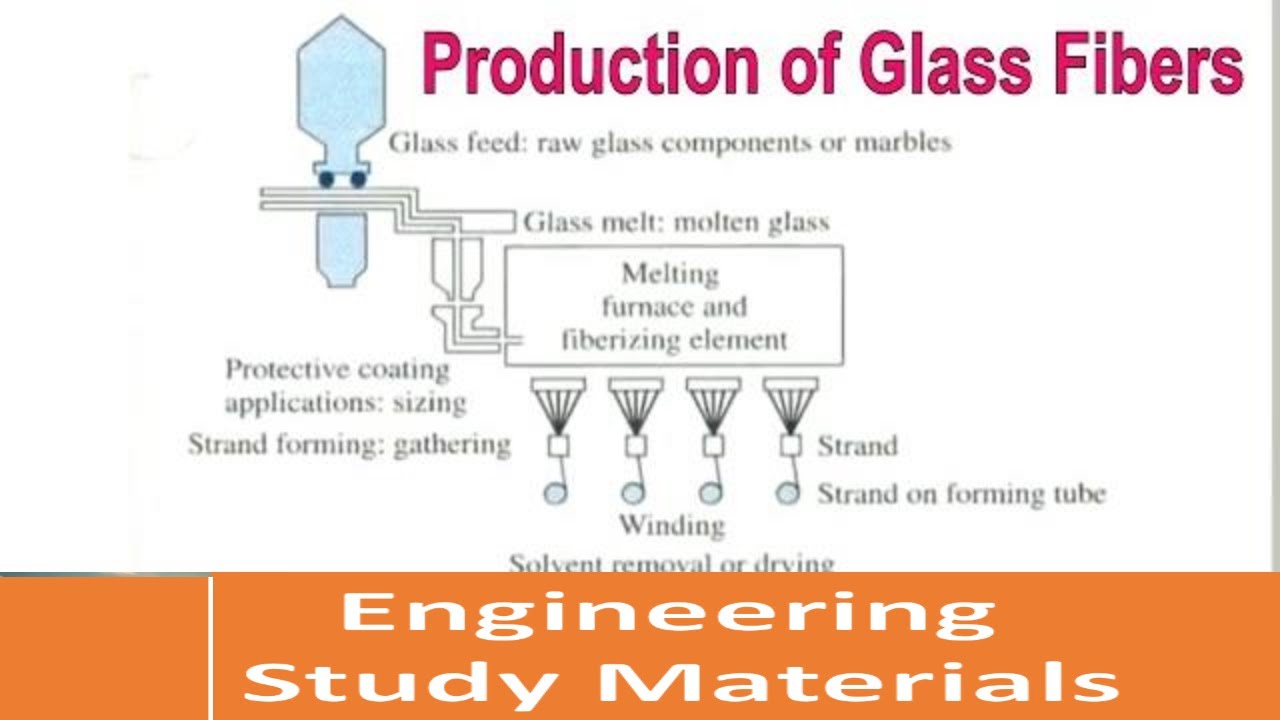
Fiber formation
Glass fiber is formed when thin strands of silica-based or other formulation glass are extruded into many fibers with small diameters suitable for textile processing. The technique of heating and drawing glass into fine fibers has been known for millennia; however, the use of these fibers for textile applications is more recent. Until this time, all glass fiber had been manufactured as staple (that is, clusters of short lengths of fiber).
The modern method for producing glass wool is the invention of Games Slayter working at the Owens-Illinois Glass Co. (Toledo, Ohio). He first applied for a patent for a new process to make glass wool in 1933. The first commercial production of glass fiber was in 1936. In 1938 Owens-Illinois Glass Company and Corning Glass Works joined to form the Owens-Corning Fiberglas Corporation. When the two companies joined to produce and promote glass fiber, they introduced continuous filament glass fibers. Owens-Corning is still the major glass-fiber producer in the market today.
Tags:
glass fiber,glass fiber manufacturing process,glass fiber reinforced concrete,glass fiber reinforced polymer,glass fiber moulding,glass fiber reinforced plastic,glass fiber types,types of glass fiber reinforced concrete,fiber,fibers,fiber production process,glass fiber nails,glass fiber bulletproof,glass fiber filament,glass fiber reinforced gypsum,high performance concrete,glass fiber manufacturing process pdf,glass fiber manufacturing process ppt
glass fiber,glass fiber manufacturing process,glass fiber reinforced concrete,glass fiber reinforced polymer,glass fiber moulding,glass fiber reinforced plastic,glass fiber types,types of glass fiber reinforced concrete,fiber,fibers,fiber production process,glass fiber nails,glass fiber bulletproof,glass fiber filament,glass fiber reinforced gypsum,high performance concrete,glass fiber manufacturing process pdf,glass fiber manufacturing process ppt