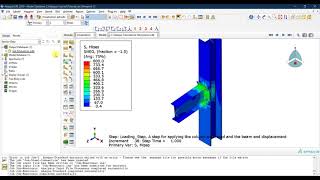
Load Switch Thyristor. Principle of OperationThyristors are often used to turn the load on and off. They are used for light bulbs, coils relays, motors. Unlike transistors, thyristors have two stable states: it is "on"-state when the thyristor resistance is minimal, and the "off"-state when the thyristor resistance is maximum. To turn the thyristor on its gate it is enough to supply control voltage shortly. To turn the thyristor off one can power-off the thyristor for a short time, change supply voltage polarity and decrease the load current below the thyristor holding current. As a rule, the thyristor switches turn on and off by two buttons. One-button thyristor control scheme is used infrequently.Let's examine a simple control circuit thyristor switch scheme as an example. In the scheme buttons without fixed position are used. Initially normally closed button contacts bypass thyristor control circuit. The thyristor resistance is maximum; no current flows through the load. To turn the thyristor on, press the button. In this case, the load is connected to a power source, capacitor C1 is charged through resistor R 1, the charge rate is determined by R1C1 time constant. When the button is released the capacitor discharges to the thyristor gate. If the voltage in it equals or exceeds the thyristor switch-on voltage, the thyristor is unlocked. The load can be switched off by short-time button clicking. Moreover, capacitor C1 does not have time to recharge. Since button contacts bypass electrodes - anode-cathode, it means that the thyristor power supply is disabled. As a result the load is off. Therefore, to enable the load it is necessary to press the control button for a long time; to turn it off - briefly press the same button again.






























































![Гелертер верят - Развитая цивилизация существовала до появления людей? [Времени не существует]](https://s2.save4k.org/pic/pMxzC99_ZkE/mqdefault.jpg)